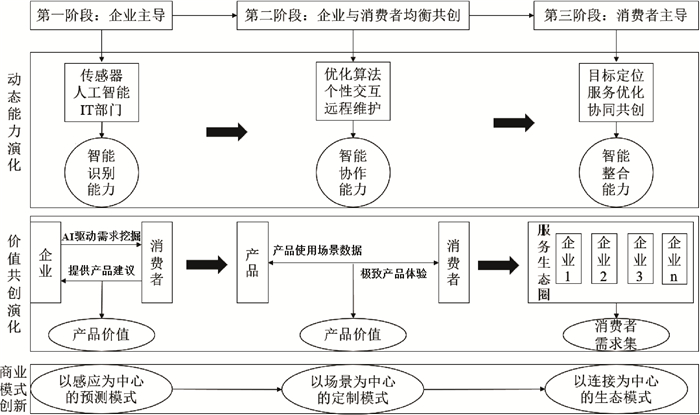
| [1] |
王飞跃. 人工智能: 第三轴心时代的来临[J]. 文化纵横, 2017(6): 94-100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4608.2017.06.015
|
| [2] |
王飞跃, 张俊. 智联网: 概念、问题和平台[J]. 自动化学报, 2017(12): 2061-2070. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MOTO201712001.htm
|
| [3] |
GEORGE G, BOCK A J. The business model in practice and its implications for entrepreneurship research[J]. Entrepreneurship Theory & Practice, 2011, 35(1): 83-111. http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=buh&AN=57367200&site=ehost-live
|
| [4] |
郑称德, 许爱林, 赵佳英. 基于跨案例扎根分析的商业模式结构模型研究[J]. 管理科学, 2011(4): 1-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JCJJ201104001.htm
|
| [5] |
庞长伟, 李垣, 段光. 整合能力与企业绩效: 商业模式创新的中介作用[J]. 管理科学, 2015(5): 31-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0334.2015.05.003
|
| [6] |
TEECE D J. Explicating dynamic capabilities: the nature and microfoundations of (sustainable) enterprise performance[J]. Strategic Management Journal, 2007, 28(13): 1319-1350. doi: 10.1002/smj.640
|
| [7] |
HELFAT C E, PETERAF M A. Managerial cognitive capabilities and the microfoundations of dynamic capabilities[J]. Strategic Management Journal, 2015, 36(6): 831-850. doi: 10.1002/smj.2247
|
| [8] |
肖新艳. 全球价值链呈现"双曲线"特征——"微笑曲线"和"彩虹曲线"[J]. 国际贸易, 2015(8): 38-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJMY201508007.htm
|
| [9] |
SIMON H A. Theories of bounded rationality[J]. Decision & Organization, 1972, 1(1): 161-176.
|
| [10] |
CHEN C F, WANG J P. Customer participation, value co-creation and customer loyalty-a case of airline online check-in system[J]. Computers in Human Behavior, 2016, 62: 346-352. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2016.04.010
|
| [11] |
迟铭, 毕新华, 徐永顺. 治理机制对顾客参与价值共创行为的影响——虚拟品牌社区的实证研究[J]. 经济管理, 2020(2): 145-159. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JJGU202002010.htm
|
| [12] |
DOZ Y L, KOSONEN M. Embedding strategic agility: a leadership agenda for accelerating business model renewal[J]. Long Range Planning, 2010, 43(2-3): 370-382. doi: 10.1016/j.lrp.2009.07.006
|
| [13] |
程鹏, 柳卸林, 李洋, 等. 本土需求情景下破坏性创新的形成机理研究[J]. 管理科学, 2018(2): 33-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JCJJ201802004.htm
|
| [14] |
李鸿磊, 黄速建. 智能化时代的商业模式特征及创新路径[J]. 经济与管理研究, 2017(6): 113-123. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JJYG201706012.htm
|
| [15] |
CASADESUS-MASANELL R, RICART J E. From strategy to business models and onto tactics[J]. Long Range Planning, 2010, 43(2): 195-215. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024630110000051
|
| [16] |
PENROSE E. Theory of the growth of the firm[J]. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 1959, 23(2): 240-241.
|
| [17] |
BARNEY J. Firm resource and sustained competitive advantage[J]. Journal of Management, 1991, 17(1): 99-120. doi: 10.1177/014920639101700108
|
| [18] |
GRANT R M. Chapter 1-the resource-based theory of competitive advantage: implications for strategy formulation[J]. Knowledge & Strategy, 1991, 33(3): 114-135.
|
| [19] |
AMIT R, SCHOEMAKER P J H. Strategic asset and organizational rent[J]. Strategic Management Journal, 1993, 14(1): 33-46. doi: 10.1002/smj.4250140105
|
| [20] |
VARGO S L, LUSCH R F. Evolving to a new dominant logic for marketing[J]. Journal of Marketing, 2004, 68(1): 1-17. doi: 10.1509/jmkg.68.1.1.24036
|
| [21] |
吴晓波, 赵子溢. 商业模式创新的前因问题: 研究综述与展望[J]. 外国经济与管理, 2017(1): 114-127. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WGJG201701009.htm
|
| [22] |
EISENHARDT K M, MARTIN J A. Dynamic capabilities: what are they?[J]. Strategic Management Journal, 2000, 21(10/11): 1105-1121. doi: 10.1002/9781405164054.ch21
|
| [23] |
ADNER R, HELFAT C E. Corporate effects and dynamic managerial capabilities[J]. Strategic Management Journal, 2003, 24(10): 1011-1025. doi: 10.1002/smj.331
|
| [24] |
BLYLER M, COFF R W. Dynamic capabilities, social capital, and rent appropriation: ties that split pies[J]. Strategic Management Journal, 2003, 24(7): 677-686. doi: 10.1002/smj.327
|
| [25] |
DIXON S E A, MEYER K E, DAY M. Stages of organizational transformation in transition economies: a dynamic capabilities approach[J]. Journal of Management Studies, 2010, 47(3): 416-436. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-6486.2009.00856.x
|
| [26] |
KLEINBAUM A M, STUART T. Network responsiveness: the social structural microfoundations of dynamic capabilities[J]. Academy of Management Perspectives, 2014, 28(4): 353-367. doi: 10.5465/amp.2013.0096
|
| [27] |
周飞, 孙锐. 基于动态能力视角的跨界搜寻对商业模式创新的影响研究[J]. 管理学报, 2016(11): 1674-1680. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-884x.2016.11.012
|
| [28] |
江积海. 商业模式创新中"逢场作戏"能创造价值吗?——场景价值的理论渊源及创造机理[J]. 研究与发展管理, 2019(6): 139-154. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJYF201906013.htm
|
| [29] |
LEE E A. Computing foundations and practice for cyber physical systems: a preliminary report[M]. Berkeley: University of California, 2007.
|
| [30] |
LIU Z, YANG D, WEN D, et al. Cyber-physical-social systems for command and control[J]. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 2011, 26(4): 92-96. doi: 10.1109/MIS.2011.69
|
| [31] |
廖建文. 撬动企业的商业生态圈[J]. 商业文化, 2016(9): 36-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYWH201609009.htm
|
| [32] |
ARTHUR D, MOTWANI R, SHARMA A, et al. Pricing strategies for viral marketing on social networks[C]//In Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop on Internet and Network Economics. New York: Springer, 2009: 101-112.
|
| [33] |
罗珉, 李亮宇. 互联网时代的商业模式创新: 价值创造视角[J]. 中国工业经济, 2015(1): 95-107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GGYY201501010.htm
|
| [34] |
宋立丰, 刘莎莎, 宋远方. 冗余价值共享视角下企业平台化商业模式分析——以海尔、小米和韩都衣舍为例[J]. 管理学报, 2019(4): 475-484. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLXB201904001.htm
|
| [35] |
李文莲, 夏健明. 基于"大数据"的商业模式创新[J]. 中国工业经济, 2013(5): 83-95. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GGYY201305006.htm
|
| [36] |
GERBERT P, JUSTUS J, HECKER M. 在AI时代快速构建竞争优势[J]. 机器人产业, 2017(5): 110-115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JQRY201705022.htm
|
| [37] |
NEUHVTTLER J, WOYKE I C, GANZ W. Applying value proposition design for developing smart service business models in manufacturing firms[C]//International Conference on Applied Human Factors and Ergonomics. Los Angeles: Springer, 2017: 103-114.
|
| [38] |
邱国栋, 甘立双. 资源依赖理论视角的隔离机制与协同效应——以三组合作研发为例[J]. 中国软科学, 2017(12): 39-48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGRK201712004.htm
|
| [39] |
OSTERWALDER A, PIGNEUR Y. Business model generation: a handbook for visionaries, game changers, and challengers[M]. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 2010.
|
| [40] |
PRAHALAD C K, RAMASWAMY V. Co-creation experiences: the next practice in value creation[J]. Journal of Interactive Marketing, 2004, 1(3): 5-14. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1094996804701073
|
| [41] |
GRÖNROOS C. Conceptualising value co-creation: a journey to the 1970s and back to the future[J]. Journal of Marketing Management, 2012, 28(13-14): 1520-1534. doi: 10.1080/0267257x.2012.737357
|
| [42] |
肖静华, 谢康, 吴瑶, 等. 企业与消费者协同演化动态能力构建: B2C电商梦芭莎案例研究[J]. 管理世界, 2014(8): 134-151, 179. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLSJ201408013.htm
|
| [43] |
PHILLIPSWREN G. AI tools in decision making support systems: a review[J]. International Journal on Artificial Intelligence Tools, 2012, 21(2): 1240005_1-1240005_13. doi: 10.1142/s0218213012400052
|
| [44] |
日经BP社信息技术媒体部. 企业人工智能战略[M]. 黄笛, 译. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2018.
|
| [45] |
KENNY D, MARSHALL J F. Contextual marketing——the real business of the Internet[J]. Harvard Business Review, 2000, 78(6): 119.
|
| [46] |
王庆金, 李如玮. 众创空间网络嵌入与商业模式创新: 共生行为的中介作用[J]. 广东财经大学学报, 2019(3): 34-42. http://song.cbpt.cnki.net/WKG/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=d0b67120-23ab-468f-99d1-be874ed68ee4
|
| [47] |
王学军, 孙炳. 变革型商业模式、双元营销能力与价值创造[J]. 广东财经大学学报, 2017(5): 34-45. http://song.cbpt.cnki.net/WKG/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=cc0fb1b5-8d53-4dba-ba2c-6370b1d3b2e9
|
| [48] |
吴瑶, 肖静华, 谢康, 等. 从价值提供到价值共创的营销转型——企业与消费者协同演化视角的双案例研究[J]. 管理世界, 2017(4): 138-157. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLSJ201704014.htm
|
| [49] |
刘建新, 李东进, 李杰. 价值共创产品依附效应的比较研究——基于心理所有权与心理流体验中介模型[J]. 管理评论, 2018(7): 114-125. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWGD201807011.htm
|





 下载:
下载: