Will American Monetary Policy Have a Spillover Effect on China's Systemic Risk: Counterfactual Analysis and Causal Intermediary Effect
-
摘要: 在全球经济金融一体化程度不断加深的过程中,对于系统性风险的防范,不仅应考虑国内经济状况的改变,更应考虑外部政策带来的溢出效应。基于2007年12月-2019年12月的数据,借助下行ΔCoES、反事实SVAR和因果中介效应模型进行实证研究,发现美国数量型货币政策的实施会对中国系统性风险形成正向溢出,而价格型货币政策的溢出影响呈非线性化;在应对美国货币政策的溢出效应时,中国价格型货币政策工具作用的平均效果大于数量型货币政策工具;美国货币政策能够通过银行和企业风险承担渠道对中国系统性风险造成溢出影响,同时企业风险承担的因果中介效率高于银行风险承担的中介效率。中国央行应与美联储之间加强协调沟通,进一步关注价格型货币政策工具在宏观经济调控以及系统性风险防范中的作用,加强宏观审慎监管,积极构建包含金融稳定的宏观审慎框架,并灵活应用货币政策工具,充分发挥国内超大规模市场优势,畅通国内大循环,以应对发达经济体货币政策变化给中国带来的溢出效应。Abstract: With the acceleration of global economic and financial integration, the prevention of systemic risk not only needs to consider the changes in the domestic economic environment, but also fully consider the spillover effect of external policies. Based on Data from December 2007 to December 2019 as research samples, systemic risk is measured with the combination of downward ΔCoES, counterfactual analysis and the causal intermediary effect model of risk-taking channel. The results show that the implementation of quantitative monetary policy in the United States will form a positive spillover to China's systemic risk, while the spillover effect of price monetary policy will be nonlinear; in dealing with the spillover effect of American monetary policy, the average effect of Chinese price-based monetary policy instruments is greater than that of quantitative-based monetary policy instruments; American monetary policy can cause spillover effect on Chinese systemic risk through bank and enterprise risk-taking channel, and the causal mediating effect rate of enterprise risk-taking is higher than that of bank risk-taking.In view of the spillover effect caused by American monetary policy, the Central Bank of China should strengthen coordination and communication with the Federal Reserve, pay more attention to the role of price-based monetary policy instruments in macroeconomic regulation and systemic risk prevention, strengthen macro-prudential supervision, actively construct a macro-prudential framework containing financial stability, and flexibly apply monetary policy instruments to give full play to domestic super-large-scale market advantages, unblock domestic large-scale cycles, and deal with the spillover effects of monetary policy in developed economies on China.
-
表 1 变量的描述性统计
变量名称 变量标识 变量解释 观测值 均值 标准差 最小值 最大值 金融部门收益率 rf 合成金融部门日收益率,用以计算月度系统性风险 3 162 0.001 8 1.250 0 -6.364 2 5.879 8 实体经济部门收益率 re 合成实体经济部门日收益率,用以计算月度系统性风险 3 162 0.000 5 3.396 8 -18.191 0 16.370 9 美国货币政策 uspmp 影子利率 145 -0.682 8 2.248 9 -5.369 2 3.608 3 美国货币政策 usqmp 美国M2对数化处理 145 9.293 3 0.211 2 8.921 2 9.636 8 中国价格型货币政策 cpmp 中国银行间7天同业拆借加权平均利率 145 3.109 6 0.969 1 0.990 0 6.981 9 中国数量型货币政策 cqmp 中国M2同比增长率 145 14.215 0 5.253 2 8.000 0 29.740 0 银行风险承担 bkrisk 不良贷款率 145 1.774 0 1.182 3 0.900 0 6.170 0 企业风险承担 corisk 研发强度=研发投入/总资产 133 6.744 9 1.171 2 4.355 8 8.316 4 政策虚拟变量 T 美联储下调其目标区间或者实行量化宽松政策时设定为1;反之为-1;若无政策调整则设定为0 145 0.062 1 0.543 0 -1 1 汇率 er 人民币兑美元汇率中间价 145 6.571 5 0.307 9 6.104 3 7.367 6 利差 sp 中国银行间7天同业拆借利率与美国联邦基准利率之差 145 -2.400 1 1.294 8 -6.888 2 0.934 5 贸易 tr 进出口金额同比增长率 145 7.738 3 16.297 8 -29.080 0 48.370 0 表 2 金融部门与实体经济部门交互风险溢出截面特征
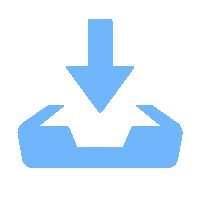
变量名称 变量标识 均值 标准差 最小值 最大值 偏度 峰度 金融部门对实体经济部门风险溢出 ΔCoESTj|i 0.128 6 0.072 3 -0.009 9 0.134 7 1.331 1 4.975 1 实体经济部门对金融部门风险溢出 ΔCoESTi|j 0.047 3 0.029 4 0.024 1 0.427 0 0.615 7 3.132 3 系统性风险 ΔCoEST 0.088 0 0.050 0 0.007 1 0.280 8 1.084 7 4.158 0 表 3 美国货币政策对中国系统性风险间接效应计算值
期数 美国数量型货币政策 美国价格型货币政策 中国价格型货币政策 中国数量型货币政策 中国数量型货币政策 当期差值 累积差值 当期差值 累积差值 当期差值 累积差值 1 -0.017 8 -0.017 8 0.006 3 0.006 3 -0.093 1 -0.093 1 2 -0.076 6 -0.094 4 -0.010 0 -0.003 7 -0.172 8 -0.265 9 3 -0.132 7 -0.227 1 -0.119 7 -0.123 3 -0.133 9 -0.399 9 4 -0.151 4 -0.378 5 -0.101 5 -0.224 8 -0.061 5 -0.461 3 5 -0.149 5 -0.528 0 -0.080 6 -0.305 4 -0.010 9 -0.472 3 6 -0.136 7 -0.664 7 -0.063 5 -0.368 9 0.016 2 -0.456 1 7 -0.119 0 -0.783 8 -0.049 8 -0.418 7 0.027 9 -0.428 3 8 -0.100 1 -0.883 8 -0.038 9 -0.457 5 0.031 0 -0.397 3 9 -0.081 8 -0.965 7 -0.030 3 -0.487 8 0.029 8 -0.367 5 10 -0.065 3 -1.031 0 -0.023 5 -0.511 3 0.026 8 -0.340 7 11 -0.051 0 -1.082 0 -0.018 1 -0.529 4 0.023 3 -0.317 4 12 -0.038 9 -1.120 9 -0.013 9 -0.543 3 0.019 8 -0.297 7 13 -0.028 9 -1.149 8 -0.010 6 -0.553 9 0.016 6 -0.281 1 14 -0.020 8 -1.170 6 -0.008 0 -0.561 9 0.013 8 -0.267 3 15 -0.014 4 -1.185 0 -0.006 0 -0.567 9 0.011 4 -0.255 9 16 -0.009 4 -1.194 4 -0.004 4 -0.572 4 0.009 4 -0.246 4 17 -0.005 5 -1.199 9 -0.003 3 -0.575 6 0.007 7 -0.238 7 18 -0.002 5 -1.202 4 -0.002 3 -0.578 0 0.006 4 -0.232 3 19 -0.000 3 -1.202 7 -0.001 6 -0.579 6 0.005 2 -0.227 1 20 0.001 2 -1.201 5 -0.001 1 -0.580 7 0.004 3 -0.222 8 注:负号表示中国货币政策在一定程度上抵减了美国货币政策对中国系统性风险影响的溢出效应。 表 4 银行或企业风险承担因果中介效应回归结果
变量 银行风险承担因果中介效应 企业风险承担因果中介效应 bkrisk sr corisk sr usmp 0.302 3*** (2.67) 0.030 1*** (3.91) -0.000 6*** (-3.19) 0.032 2** (4.79) bkrisk 0.001 0*** (1.63) corisk -7.681 3*** (-2.78) sp 0.256 6*** (3.49) 0.016 7*** (3.28) -0.000 5 (-3.87) 0.015 7*** (3.36) tr -0.000 6 (-0.18) -0.000 8*** (-3.27) 0.000 0 (-0.98) -0.000 7*** (-3.43) er 0.489 3 (1.62) -0.039 7** (-1.96) -0.000 2 (-0.42) -0.032 8** (-1.73) 常数项 -0.937 4 (-0.44) 0.380 0*** (2.70) 0.020 8*** (5.11) 0.505 9*** (3.50) N 145 145 145 145 R2 0.295 8 0.260 1 0.283 8 0.329 1 平均中介效应 0.002 9*** 0.004 8*** 直接效应 0.030 4*** 0.032 4*** 总效应 0.033 3*** 0.037 2*** 中介效应率(%) 8.76 12.93 注:括号内数字为t值;*p < 0.1,**p < 0.05,***p < 0.01;通过1 000次准贝叶斯蒙特卡罗逼近仿真获得中介效应、直接效应、总效应和中介效应率,其中,中介效应率=中介效应/总效应。下表同。 表 5 银行或企业风险承担因果中介效应稳健性回归结果
变量 银行风险承担因果中介效应 企业风险承担因果中介效应 bkrisk sr corisk sr usmp -0.142 4*** (-2.70) 0.030 3*** (4.79) 0.009 8*** (3.20) 0.015 5** (2.18) bkrisk -0.047 5*** (-4.80) corisk 1.334 2*** (6.35) sp -0.226 4*** (-6.26) 0.009 0** (1.88) 0.005 0*** (2.78) 0.016 1*** (3.88) tr 0.002 4 (1.32) -0.000 6*** (-2.82) -0.000 0 (-0.82) -0.000 2 (-0.77) er -0.824 1*** (-5.35) -0.070 0*** (-3.54) -0.037 5*** (-4.72) -0.001 7 (-0.09) 常数项 6.854 0 (6.34) 0.671 7*** (4.69) 0.306 9*** (5.49) 0.078 6 (0.56) N 145 145 145 145 R2 0.707 1 0.392 5 0.220 1 0.463 7 平均中介效应 0.006 7*** 0.013 1*** 直接效应 0.030 5*** 0.015 7*** 总效应 0.047 2*** 0.028 8*** 中介效应率(%) 18.03 45.73 -
[1] 杨子晖, 陈里璇, 陈雨恬. 经济政策不确定性与系统性金融风险的跨市场传染--基于非线性网络关联的研究[J]. 经济研究, 2020(1): 65-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JJYJ202001006.htm [2] BORIO C, ZHU H. Capital regulation, risk-taking and monetary policy: a missing link in the transmission mechanism[J]. Journal of Financial Stability, 2012, 8(4): 236-251. doi: 10.1016/j.jfs.2011.12.003 [3] TILLMANN P, KIM G Y, PARK H. The spillover effects of U.S. monetary policy on emerging market economies[J]. International Journal of Finance and Economics, 2019, 24(3): 1313-1332. doi: 10.1002/ijfe.1720 [4] 易晓溦, 陈守东, 刘洋. 美国非常规货币政策冲击下中国利率期限结构动态响应研究[J]. 国际金融研究, 2015(1): 25-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJJR201501004.htm [5] BOWMAN D, LONDONO J M, SAPRIZA H. U.S. unconventional monetary policy and transmission to emerging market economies[J]. Journal of International Money and Finance, 2015, 55: 27-59. doi: 10.1016/j.jimonfin.2015.02.016 [6] 余振, 张萍, 吴莹. 美国退出QE对中美两国金融市场的影响及中国的对策--基于FAVAR模型的分析[J]. 世界经济研究, 2015(4): 24-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JING201504004.htm [7] 谭小芬, 李源, 苟琴. 美国货币政策推升了新兴市场国家非金融企业杠杆率吗?[J]金融研究, 2019(8): 38-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JRYJ201908003.htm [8] 乔木子, 宋玉臣. 发达经济体货币政策对我国系统性金融风险的外部冲击效应研究[J]. 经济纵横, 2018(3): 114-122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JJZH201803014.htm [9] 谷慎, 汪淑娟, 胡耀平. 美国货币政策对中国金融稳定的影响研究[J]. 上海经济研究, 2019(10): 117-128. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HSYJ201910013.htm [10] 路妍, 李爽. 美欧英日货币政策冲击对系统性金融风险的影响研究[J]. 武汉金融, 2020(11): 13-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3540.2020.11.002 [11] CHORTAREAS G, NOIKOKYRIS E. Federal reserve's policy, global equity markets, and the local monetary policy stance[J]. Journal of Banking and Finance, 2017, 77(3): 317-327. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378426616300589 [12] 张晓慧. 多重约束下的货币政策传导机制[M]. 北京. 中国金融出版社, 2020: 349-374. [13] 金春雨, 张龙. 美联储货币政策对中国经济的冲击[J]. 中国工业经济, 2017(1): 25-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GGYY201701003.htm [14] 安蕾. 资本流动在美国货币政策向新兴市场传导中的作用[J]. 国际经贸探索, 2019(10): 91-107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJTS201910006.htm [15] 王正新, 姚培毅. 中国经济政策不确定性的跨国动态溢出效应[J]. 中国管理科学, 2019(5): 78-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGK201905009.htm [16] 崔百胜, 葛凌清. 中国货币政策对世界主要经济体溢出效应的异质性分析--基于GVAR模型的实证研究[J]. 华东经济管理, 2019(8): 83-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDJJ201908012.htm [17] KAZI I A, WAGAN H, AKBAR F. The changing international transmission of U.S. monetary policy shocks: is there evidence of contagion effect on OECD countries[J]. Economic Modelling, 2013, 30: 90-116. doi: 10.1016/j.econmod.2012.07.020 [18] GILBERT C, GREGORY L, ALEXANDRA P. Monetary policy and long-run systemic risk-taking[J]. Journal of Economic Dynamics and Control, 2018, 86: 165-184. doi: 10.1016/j.jedc.2017.11.001 [19] BRUNO V, SHIN H S. Capital flows and the risk-taking channel of monetary policy[J]. Journal of Monetary Economics, 2015(2): 119-132. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304393214001688 [20] BRUNNERMEIER M K, SANNIKOV Y. A macroeconomic model with a financial sector[J]. American Economic Review, 2014, 104(2): 379-421. doi: 10.1257/aer.104.2.379 [21] DEWACHTER H, WOUTERS R. Endogenous risk in a DSGE model with capital-constrained financial intermediaries[J]. Journal of Economic Dynamics and Control, 2014, 43(3): 241-268. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0165188914000633 [22] 梁琪, 李政, 郝项超. 我国系统重要性金融机构的识别与监管--基于系统性风险指数SRISK方法的分析[J]. 金融研究, 2013(9): 56-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JRYJ201309005.htm [23] 杨子晖, 陈雨恬, 谢锐楷. 我国金融机构系统性金融风险度量与跨部门风险溢出效应研究[J]. 金融研究, 2018(10): 19-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3109.2018.10.004 [24] 李政, 梁琪, 方意. 中国金融部门间系统性风险溢出的监测预警研究--基于下行和上行ΔCoES指标的实现与优化[J]. 金融研究, 2019(2): 40-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JRYJ201902003.htm [25] 李政, 刘淇, 梁琪. 基于经济金融关联网络的中国系统性风险防范研究[J]. 统计研究, 2019(2): 23-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJYJ201902003.htm [26] ADRIAN T, BRUNNERMEIER M K. CoVaR[J]. American economic review, 2016, 106(7): 1705-1741. doi: 10.1257/aer.20120555 [27] BACHMANN R, SIMS E R. Confidence and the transmission of government spending shocks[J]. Journal of Monetary Economics, 2012, 59(3): 235-249. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoneco.2012.02.005 [28] IMAI K, KEELE L, YAMAMOTO T. Identification, inference and sensitivity analysis for causal mediation effects[J]. Statistical Science, 2010, 25(1): 51-71. http://thorax.bmj.com/lookup/external-ref?access_num=10.1214/10-STS321&link_type=DOI [29] 余升国, 郭文璇, 胡婧玮. 美国量化宽松货币政策对中国宏观经济的影响--基于TVP-VAR模型的分析[J]. 经济问题, 2018(7): 85-91. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JJWT201807014.htm [30] 崔百胜, 高崧耀. 二十国集团货币政策溢出效应的非对称性与异质性研究--基于PCHVAR模型[J]. 国际金融研究, 2019(12): 33-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJJR201912004.htm [31] 蒋海, 张小林, 刘敏. 货币政策影响银行风险承担的杠杆机制检验[J]. 世界经济研究, 2019(3): 3-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JING201903002.htm [32] LI K, GRIFFIN D, YUE H, et al. How does culture influence corporate risk-taking?[J]. Journal of Corporate Finance, 2013, 23(12): 1-22. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0929119913000655 [33] 余明桂, 李文贵, 潘红波. 管理者过度自信与企业风险承担[J]. 金融研究, 2013(1): 149-163. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JRYJ201301014.htm [34] BRUNO V, SHIN H S. Cross-border banking and global liquidity[J]. The Review of Economic Studies, 2014, 82(2): 535-564. http://restud.oxfordjournals.org/content/early/2014/12/11/restud.rdu042.abstract [35] 方意, 陈敏. 经济波动、银行风险承担与中国金融周期[J]. 世界经济, 2019(2): 3-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJJJ201902002.htm [36] 周彬蕊, 刘锡良, 张琳. 货币政策冲击、金融市场化改革与企业风险承担[J]. 世界经济, 2017(10): 93-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJJJ201710006.htm [37] 孙静, 许涛, 俞乔. 混业经营下的系统性金融风险及防控[J]. 江淮论坛, 2019(1): 37-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JHLZ201901007.htm [38] 聂菁, 金洪飞. 美国量化宽松货币政策对中国行业出口的溢出效应研究[J]. 国际金融研究, 2015(3): 3-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJJR201503001.htm [39] 陈虹, 马永健. 美国量化宽松货币政策与退出效应及其对中国的影响研究[J]. 世界经济研究, 2016(6): 22-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JING201606004.htm [40] 付英俊. 全球银行借贷流动、货币政策国际风险承担与宏观审慎管理[J]. 国际金融, 2020(3): 36-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JRGJ202003005.htm -





 下载:
下载: